In the fast-paced digital era, businesses face an ever-increasing demand to adapt and innovate quickly. Traditional software development, often hindered by lengthy timelines and resource constraints struggles to meet these accelerated needs. Enter low-code development - a game-changer poised to transform how we build applications.
This game-changing approach is empowering individuals and businesses to create custom applications faster and easier than ever before.

As adoption skyrockets, market research confirms that this is more than a passing trend. Grand View Research estimates that the global low‑code application development platform market was worth USD 24.83 billion in 2023 and projects it will reach USD 101.68 billion by 2030—a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.5%. The same report notes that low‑code and no‑code tools address talent shortages by letting organizations build systems without hiring large teams of developers, and that by 2024, 80 % of non‑IT professionals are expected to develop IT products and services, with over 65 % using low‑code/no‑code tools. These statistics underscore how low‑code and no‑code development are becoming mainstream drivers of digital transformation.
What is Low-Code?
- It's a visual development approach that minimizes the need for traditional hand-coding.
- It leverages drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-built templates, and intuitive tools.
- It enables even those with limited coding experience to build powerful applications.
Low‑code platforms reduce but don’t eliminate the need for coding, making them ideal when some customization is required; no‑code tools aim to remove coding entirely and empower non‑technical users to create applications without writing any code.
Low‑Code vs. No‑Code at a Glance
- Low‑Code Platform – Users can create applications quickly but may need to write small amounts of code for complex functionality.
- No‑Code Platform – Designed for users with no coding knowledge; the entire development process relies on visual drag‑and‑drop and configuration.
- Pro‑Code Development – Traditional hand‑coding by professional developers for bespoke, highly complex applications.
Top Low-Code Platforms
According to the Gartner Report on Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms, the following is the list of top low-code Platforms
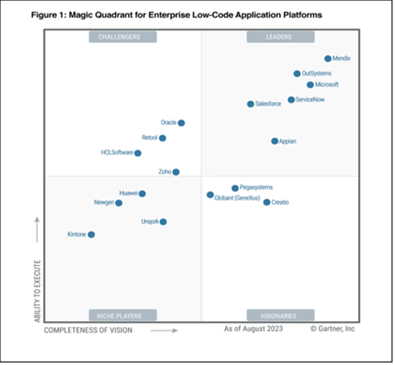
- Mendix
- OutSystems
- Microsoft Power Apps
- ServiceNow
- Salesforce
- Appian
- Pegasystems
These leading low‑code application development platforms are often marketed as the best app builders without coding or no‑coding app builders, reflecting their ability to empower both professional developers and business users. For example, Microsoft Power Apps integrate seamlessly with Office 365 and Dynamics 365, making it popular for enterprise low‑code solutions.
Key Advantages to Developers
1. Rapid Development Time and Easy to Use
As low-code platforms provide visual interfaces, pre-built components, and drag-and-drop functionality for building the front and back end of applications - it streamlines the development process and helps developers to build apps faster.
Let’s see an example of creating a List Screen in OutSystems using drag-and-drop functionality
Open Main Flow Interface Tab
Go to the Data tab, and drag and drop your entity inside the MainFlow, then enjoy the magic show.
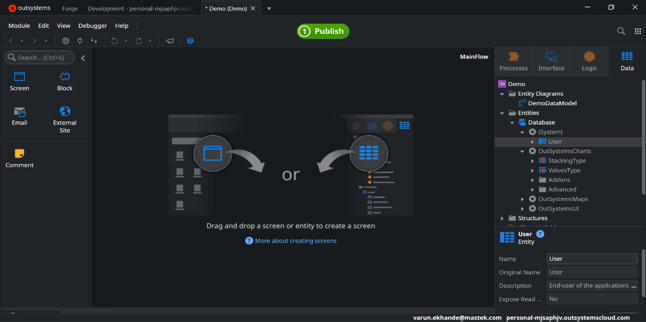
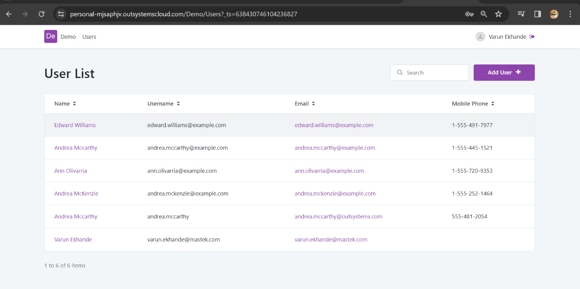
OutSystems has created a user screen for me just by drag and drop:
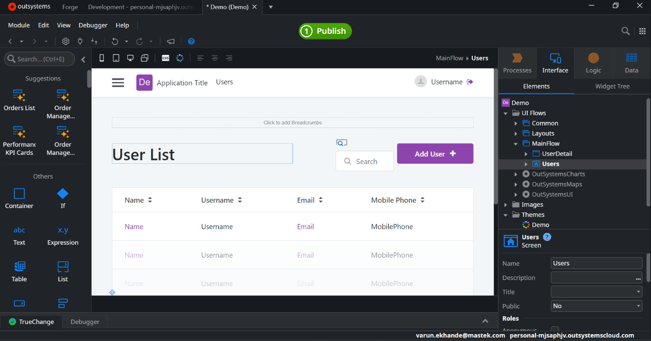
Here is the output of the screen:
2. Learning Curve (Training and Documentation)
The learning curve for developers getting started with low-code platforms is fairly modest. Most of the major platforms like PowerApps, Mendix, and OutSystems provide a significant amount of training materials for developers and there is a large base of documentation and community support which provides a helping hand for developers during the development process.
For example, OutSystems provide guided paths from which developers can choose their low-code journey, I have heavily used it in my initial years while using OutSystems.
3. Cross-Platform Deployment
Many low-code platforms allow you to deploy apps to multiple platforms like the web, mobile (IOS and Android) and desktop which are developed using a single codebase. This reduces the effort spent on porting code
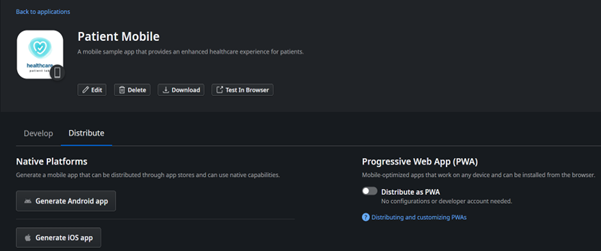
Here is an example in OutSystem: I have a patient app developed using a single code base, and the platform allows me to distribute the application as an Android app or an IOS app.
4. Integration Capabilities
Low-code platforms provide components, integration builders and the ability to integrate databases and connect to other Systems using REST API capabilities. It simplifies and makes it less complex for developers while doing the integration development.
5. Boosted Developer Productivity
By automating repetitive coding tasks and providing reusable components, low‑code tools free developers to focus on higher‑value work. This is one reason why low‑code is viewed as strategic.
6. Empowering Citizen Developers and Collaboration
Low‑code platforms democratize app creation by turning business professionals into citizen developers. According to KPMG’s 2024 report, 47 % of surveyed organizations have or plan to establish low‑code guidelines and defined governance, illustrating that enterprises are formalizing citizen‑development programs.
7. Enhanced Workflow Automation
Built‑in workflow automation capabilities orchestrate approvals, notifications and data integration, further accelerating delivery.
Accelerating Innovation and Time–to–Market
Visual interfaces, pre-built components, and drag-and-drop functionality streamline the development process, significantly reducing time-to-market for applications. This enables organizations to quickly respond to evolving market demands, seize opportunities, and stay ahead of the competition.
Key Advantage of Using Low-Code Approach
- Accelerated Delivery: build and deploy apps in weeks or even days, not months.
- Enhanced Agility: respond to evolving business needs rapidly and efficiently.
- Reduced Costs: lower development costs and faster time-to-market lead to significant savings.
- Enhanced Agility: adapt and iterate quickly to meet changing needs and market trends.
Common Use – Cases for Low-Code Platforms
- Marketing: create personalized customer journeys and automate marketing campaigns.
- HR: streamline recruitment, onboarding, and employee training processes.
- Finance: automate financial workflows and generate insightful reports.
- Sales: build custom CRMs and sales management tools.
- Operations: optimize supply chain management and inventory tracking.
Reduce Cost of Ownership Using Low-Code Approach
Traditional app development is expensive. Hiring skilled developers, acquiring expensive software licenses, and dealing with ongoing maintenance costs can quickly drain your resources. Low-code platforms offer a more cost-effective alternative:
- Subscription-based pricing: pay a predictable monthly or annual fee, eliminating the need for upfront investments.
- Reduced development time: get your app up and running faster, minimizing labour costs.
- Simplified maintenance: low-code platforms often handle updates and security patches, lowering ongoing IT expenses.
Future of Low-Code
The outlook for low-code platforms is stronger than ever. Industry research shows that a majority of organizations now see low-code as a strategic driver of digital transformation, and adoption is accelerating worldwide. While challenges such as security and customization remain, these can be addressed through careful platform selection and solid governance.
As the technology evolves, integrations with AI and machine learning will unlock even greater automation, smarter analytics, and faster innovation. These advancements align directly with ai for digital engineering, empowering teams to engineer smarter solutions, accelerate development cycles, and deliver scalable digital products. With the market projected to grow significantly through 2030, low-code is set to remain a powerful catalyst for agility, creativity, and competitive advantage in the years ahead.