Agility in decision-making processes is the buzzword in the ever-changing and dynamic business environment. In my view, businesses want to act and improve their decision-making in real time. One of the important factors to bring agility to business decisions is to have effective, actionable insights on information available to business in days or weeks and not in months or years.

This article highlights some of the modern world business concerns, needs and expectations in the context of Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Warehouse (DW) solutions. Some of these concerns are indeed difficult to address with traditional DW and BI solutions, due to inherent complex design structures and delivery timescales. You will gain insights into how these challenges will be addressed and expectations met with technologies like Data Virtualisation (DV) to deliver Agile BI solutions.
Key Concerns, Needs and Expectations
- Does the existing data warehouse meet my BI requirements? How can I extend or augment my existing data warehouse easily and quickly?
- I want real time insights for business decisions. Does the existing reporting and BI solution provide me real time reporting and analytics?
- I have new business requirements which necessitate changing source data structures. Can this be reflected directly in my data marts for BI purposes?
- I need an interim reporting and dashboard solution until my EDW and BI is built? Can this be provided in an agile way?
- While I require audit, governance, security and data lineage, I want an out-of-the-box solution.
Challenges with Traditional EDW approach
Enhancing an existing EDW is laborious and time-consuming
Organisations strive to build Enterprise Data Warehouses (EDW) as a one source for reporting. However, each department or business function knows that there will always be a need to augment the EDW with department-specific datasets. In the traditional approach, augmentation of EDW with department data sets is generally managed through an ad-hoc ETL process of re-loading some of the EDW data into department Personal Data Stores (PDS). Reports are created on PDS according to the needs of different stakeholders and are not shared across department or business functions.
This approach is time-consuming, increases latency, security concerns, cannot guarantee single version of truth and results in data duplication. The diagram below depicts information landscape of a typical organisation which has Personal Data Store (PDS) as a data source to generate department specific reports.
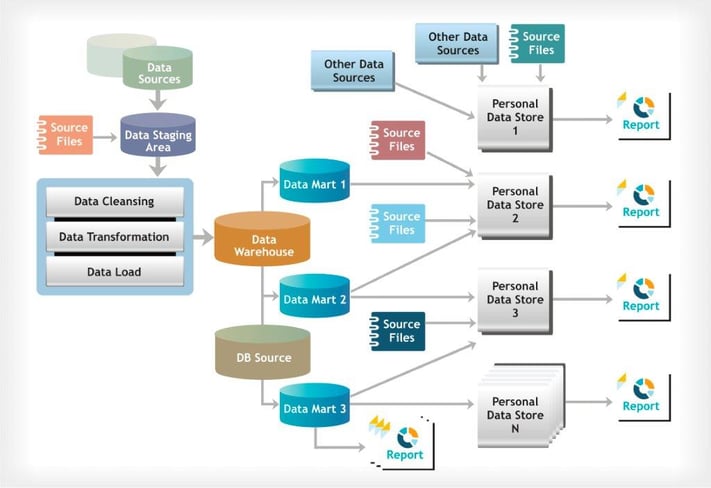
Figure 1: Enterprise Information Landscape: Data warehouse & Personal Data Store
Longer implementation timelines with no interim solution
Longer implementation timelines for EDW are a concern for many organisations. Often, individual decision-makers need immediate access to reports and dashboards as EDW process completion takes longer time, and requires interim solutions as a result.
Real-time/Near Real-time reporting
Real-time reporting/Near Real-time reporting is a key challenge in the traditional data warehouse approach as data has to be loaded into the EDW resulting in latency.
1. Potential Solution: Data Virtualisation
Data virtualisation (DV) technology is the potential solution for addressing the issues specified above, as well as to serve as a platform of choice for delivering Agile BI. DV offers an approach to data management, facilitating data integration without replicating or loading data from source systems or source files. DV makes it possible to create an enterprise ‘virtual’ data layer on top of the source data (including the EDW itself) that can be further accessed by reporting applications downstream in real-time or near real-time.
Such a solution will result in quicker access to all data, reduce development and implementation timelines, minimise data replication, reduce cost, and bring agility to adjust according to new business needs. The diagram below depicts the Reference Architecture for data virtualisation implementation, to address enterprise reporting and BI needs.
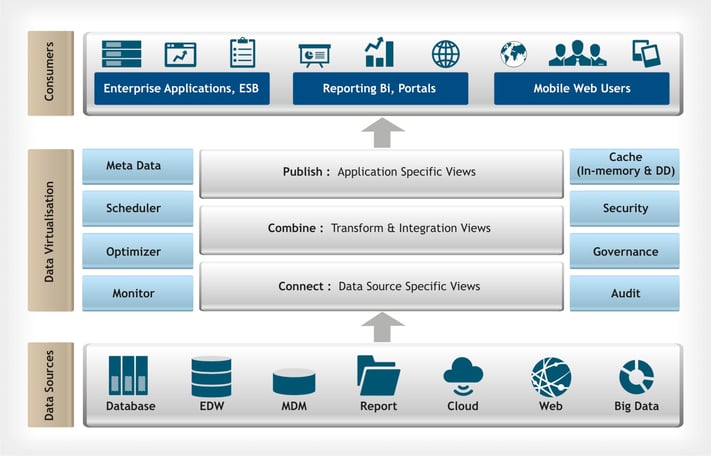
Figure 2: Reference Architecture: Data Virtualisation
2. Server Environment Elements
The key architectural elements of data virtualisation based solutions are described below.
- Connectors: DV tool can connect to any type of data source from structured, semi-structured to even unstructured.
- DV Logical Layer: This layer represents enterprise data model and represents single version of truth. When a report is generated, data moves from data sources through the layers of these views cleansing, transforming and joining before producing the report.
- Cache: The resultant set of DV views can be cached in-memory or in any standard database, e.g. Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, etc.
- Optimiser: DV supports cost-based and rule-based query optimisation for seamless information flow across views and allows creation of indexes on data virtual layer.
- Security: In addition to standard authorisation and authentication mechanism, DV supports multi-tenancy and supports row and column level security.
- Audit: DV keeps an audit traceability of what, when and who accessed the DV layer. The audit traceability is maintained in a repository, which can be configured in any standard database e.g. Oracle, Postgre, SQL server etc.
- Metadata: DV tools maintain metadata of connection details, DV object definition, security information etc. in the repository.
3. Technologies and tools
Some of the leading providers of DV technologies are:
- CISCO Data Virtualisation
- Denodo platform
- Red Hat Data Virtualisation & Data Grid
- Informatica Data Virtualisation
Data Virtualisation is a highly efficient way to provide a self-service reporting solution to business stakeholders in real-time by combining data from operational systems, multiple local silos and existing data from data warehouses.
At Mastek, we believe that Data Virtualisation solutions will deliver faster ROI and agility in decision-making based on actionable insights. As an alternative/complementary to big bang Data Warehouse solutions, DV offers a lightweight, cost-effective BI solution in a rapidly changing market place.

